From Table 3, it can be seen that the load of factors 2 and 4 is the largest. They are the main factors affecting the stability and play a decisive role in the stability of the product. Factor 2 is mainly composed of urea aldehyde ratio. Factor 4 is mainly composed of linear ratio of starch to water, hydrolysis time, oxidation pH, oxidation time and oxidant dosage. That is, the ratio of starch to water, the degree of oxidation of oxidized starch, and the urea-aldehyde ratio have a great influence on the stability of the modified urea-formaldehyde adhesive.
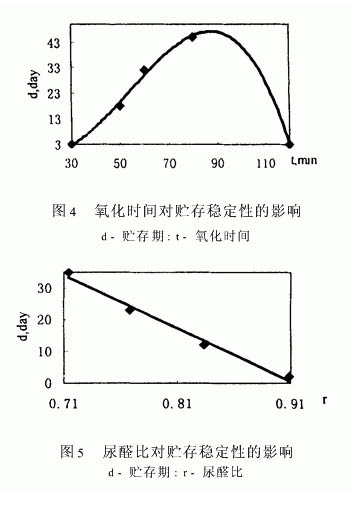
As shown in Figure 4, the effect of the oxidation time on storage stability is in the form of an open downward parabola. At the initial stage of the reaction, the storage stability increases with the extension of the oxidation time, but the oxidation time is too long and the storage stability decreases. Because in a certain oxidation time, starch is oxidized to aldehyde, and aldehyde under suitable conditions can condense with hydroxy that causes poor stability of urea-formaldehyde resin to generate hemiacetal or acetal which is more stable to alkali and oxidant, increasing Urea urea rubber stability. If the degree of oxidation of the starch is too large, the reactive groups in the reaction system are too much, on the one hand, the gelation phenomenon easily occurs, and on the other hand, the solid content of the product is too high, resulting in a decrease in the stability of the urea-formaldehyde glue.
Selecting a suitable urea-formaldehyde ratio also helps to increase the stability of the urea-formaldehyde adhesive. As shown in FIG. 5, as the urea-aldehyde molar ratio increases (the number of moles of formaldehyde decreases), the stability of the urea-aldehyde resin decreases. Because in the low molar ratio of urea-formaldehyde resins, the content of methylene groups is high, and there are more amino and imino groups that do not participate in the reaction. These groups are relatively active and have strong reactivity, which reduces the stability of the product. At a high molar ratio, more dimethylol urea is formed in the reaction, and more methylol groups are contained in the product, and ether bond compounds are even present, thereby enhancing the stability of the resin.
2.4 Main Factors Affecting Adhesive Strength


From Table 4, it can be seen that the main factor that influences the shear force performance is factor 4, which is the hydrolysis pH, the hydrolysis time, the amount of oxidant, and the ratio of starch to urea. This is consistent with the results of the literature on the performance of urea-formaldehyde adhesives. That is, for oxidized starch-modified urea-formaldehyde resins, the degree of hydrolysis, oxidation of oxidized starch, and the amount of oxidized starch added are the key factors affecting the adhesive strength of the product. The effect of the amount of oxidized starch on the adhesive strength of urea-formaldehyde resin is shown in Figure 6. In a certain range, the shear strength increases with the addition of oxidized starch; but after the addition of oxidized starch reaches a certain level The change in shear strength is not so obvious. From the regression equation, it shows a downward trend. The reason for this phenomenon is that the main cross-linking action during the curing process is the hydroxyl group. Part of the unoxidized hydroxyl groups in the oxidized starch not only cross-link to each other but also form bonds with the hydroxyl groups and aldehyde groups in the board. The role of urea-formaldehyde resin cementation strength has been enhanced. On the other hand, the bonding strength is also affected by the wettability of the board, the board has low wettability, the glue quality is poor, the wetting property is high, and the glue quality is good. For urea-formaldehyde resin modified by oxidized starch, its surface tension gradually increases with the increase of the amount of oxidized starch added. As the surface tension increases, the contact angle increases, the wettability of the plate decreases, and the bonding quality deteriorates.
3 Conclusion
(1) The starch type, urea-aldehyde ratio, and the extent of starch oxidation have a greater impact on free formaldehyde content. The extent to which starch is oxidized has the greatest effect on free formaldehyde content.
(2) Urea-formaldehyde ratio, starch type, hydrolysis time and oxidation degree have a greater impact on the solid content.
(3) The ratio of starch to water, the degree of oxidation of starch and the urea-aldehyde ratio have the greatest effect on the stability of modified urea-formaldehyde rubber.
(4) The main factors affecting the adhesive strength of modified urea-formaldehyde resin are the factors such as the degree of hydrolysis and oxidation of starch and the amount of oxidized starch added.
Source: 21st Century Fine Chemicals Network
Pet Clothes,Dog Clothes,Cat Clothes,Pet lovers clothing,Dog Shirt
Ningbo Yinzhou Hengxi Winbate Household Product Manufacturer , https://www.winbatehousehold.com