introduction
Van der Waals crystals, including graphene, boron nitride, transition metal chalcogenides and other new two-dimensional materials, which have attracted much attention, have excellent mechanical, electrical and optical properties, and are the basic unit for constructing functionally controlled van der Waals heterojunctions. It is also the basic material for the next generation of high performance optoelectronic devices.
Van der Waals crystals have a layered structure, which is bonded by strong covalent bond interactions within the layer and combined by weak van der Waals forces between the layers. This layered structure determines the natural anisotropy of various physical properties of van der Waals crystals. Among them, optical anisotropy is essential for the design and optimization of new optoelectronic devices and must be accurately characterized. However, due to the size of high-quality van der Waals single crystals, traditional optical anisotropy characterization methods based on far-field beam reflection, such as end-reflection and ellipsometry, cannot accurately characterize the optical orientation of van der Waals microcrystals. opposite sex.
Result introduction
Recently, the research team of the Nano characterization laboratory of the National Nanoscience Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dai Qing (a user of Quantum Design China subsidiary), used German neaspec near-field optical technology to overcome the difficulties caused by the limited size of the above-mentioned van der Waals crystals, and successfully measured boron nitride and two. The dielectric constant tensor of molybdenum sulfide.
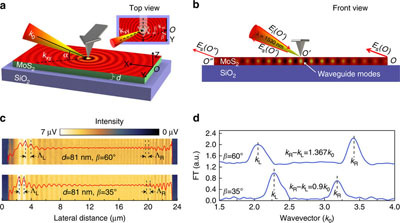
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of experimental device and near-field imaging principle
The team first theoretically demonstrated the existence of unusual and extraordinary waveguide modes in anisotropic van der Waals nanosheets. The in-plane wavevectors of the two modes are related to the in-plane and out-of-plane dielectric constants of van der Waals crystals respectively; neaSNOM scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy, exciting ordinary and extraordinary waveguide modes in van der Waals nanosheets, and real-field near-field optical imaging of these waveguide modes; finally, they are close to real space by nanoFTIR nano-Fourier infrared module The Fourier analysis of the field optical image was used to obtain the optical anisotropy of the measured van der Waals crystal.
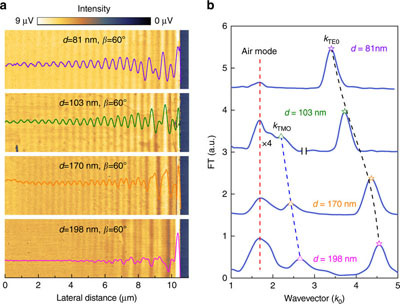
Fig. 2 Near-field optical image and Fourier analysis of MoS2 samples with different thicknesses
in conclusion
This method overcomes the limitation of sample size by traditional characterization methods, and can accurately characterize the optical anisotropy of uniaxial and biaxial van der Waals crystal materials. This method is expected to be used for small layers by optimizing the design of substrate materials. Direct characterization of optical anisotropy of even single-layer van der Waals crystals. The results of the study were published online in Nature Communications, and the characterization method has applied for a patent for invention. Relevant research work has been funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Youth Thousand Talents Program.
References: Probing optical anisotropy of nanometer-thin van der waals microcrystals by near-field imaging (Nat. Commun., 2017, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01580-7)
Source: National Nano Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences
neaSNOM little knowledge, how much do you know?
The neaSNOM scattering near-field optical microscope uses a patented scattering core design technology that greatly enhances optical resolution and is independent of the wavelength of the incident laser, providing superior performance in the visible, infrared, and terahertz spectral range. Spectral and near-field optical images with 10 nm spatial resolution ensure high reliability and repeatability.
Technical features and advantages:
? Patented scattering near-field optical measurement technology
Patented high-order demodulation background compression technology
Patented Interferometric Near Field Signal Detection Unit
Patented helium heterodyne interferometric detection technology
? Patented reflective optical system
High stability AFM system dual beam design
nano-FTIR - the bar of nano-infrared characterization
nano-FTIR nano-Fourier infrared spectroscopy combines the high spatial resolution of atomic force microscopy with the high chemical sensitivity of Fourier infrared spectroscopy, enabling chemical resolution of virtually all materials at the nanoscale. Moreover, under the condition of no model correction, the molecular fingerprint characteristics of the near-field absorption spectrum obtained by nano-FTIR are highly consistent with the molecular fingerprint features obtained by the traditional FTIR spectrometer, which is important in basic research and practical application. significance.
Stainless Steel Vacuum Sports Bottle
Stainless Steel Bottles are made from high-grade 18/8 stainless steel. This material is food grade, non-toxic, durable and easy to clean.
Our Stainless Steel Bottles are mostly Stainless Steel Vacuum Water Bottles. They have a double-wall vacuum treatment, so they can ensure your drink keeps as it is. And you don't need to worry about getting your hands cold or hot.
Stainless Steel Vacuum Sports Bottle,Solid Color Insulated Sports Water Bottle,Solid Color Vacuum Sports Water Bottle,Heat Transfer Vacuum Sports Water Bottle
Ningbo Auland International Co.,Ltd. , https://www.everdrinkingbottle.com